HashMap是我们平时开发中用的比较多的集合容器,但是它不是线程安全的。当需要在多线程时保证安全我们会选择使用ConcurrentHashMap。下面对这两个集合介绍(基于Java8的源码,同时会与Java7的简单对比)。
HashMap
Java8的HashMap底层结构是基于数组+链表/红黑树,相比Java7多了一个红黑树。红黑树主要解决了当冲突过多,链表太长,查询时间复杂度会变成O(N)的问题,Java8中当链表存储元素大于8之后将转成红黑树的存储方式,这样最坏时间复杂度由O(N)变成了O(logN)。
下图是HashMap的简单结构示意图: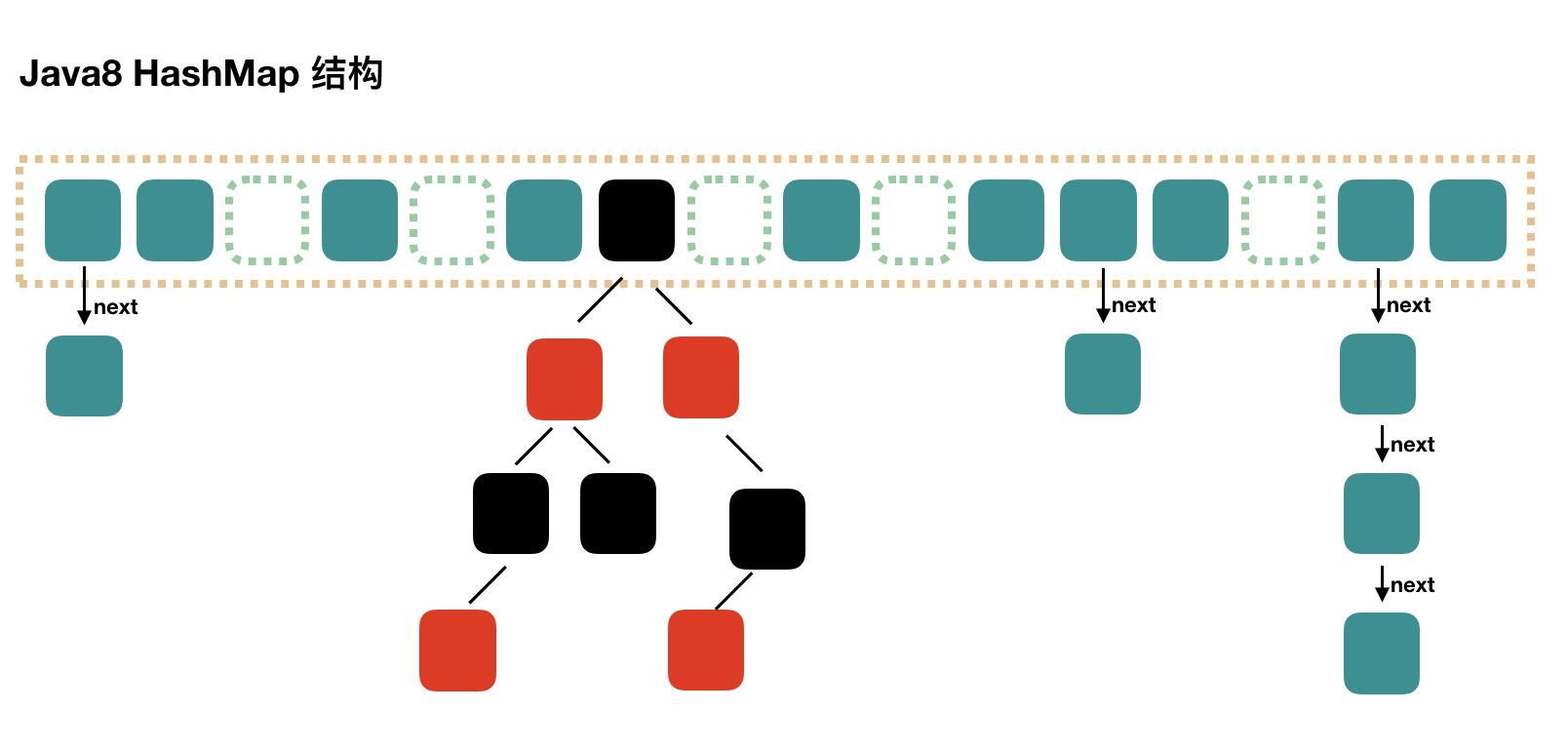
Java7 中使用 Entry 来代表每个 HashMap 中的数据节点,Java8 中使用 Node,基本没有区别,都是 key,value,hash 和 next 这四个属性,不过,Node 只能用于链表的情况,红黑树的情况需要使用 TreeNode。我们根据数组元素中,第一个节点数据类型是 Node 还是 TreeNode 来判断该位置下是链表还是红黑树的。
常量介绍
1 | static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; //默认容量16 |
put方法分析
1 | public V put(K key, V value) { |
扩容resize方法分析
1 | final Node<K,V>[] resize() { |
get方法分析
HashMap的get操作相当简单,根据key的hash值去数组中找对应的位置的node,如果该位置第一个元素就是要找的就直接返回,否则判断node是红黑树还是链表,遍历红黑树或者链表找到对应的value返回。
1 | public V get(Object key) { |
HashMap线程不安全的体现
- 多个线程同时插入时,如果两个键的hash冲突了,有可能同时操作同一个结点,会造成数据覆盖的问题。
- 扩容时,会新建一个table,然后把数据迁移到新的table,如果在迁移时有线程来获取数据,就会造成获取数据为空。
hashCode的计算
1 | static final int hash(Object key) { |
HashMap的hash值都是通过将key的hashCode()高16位与低16位进行异或运算,这样可以保留高位的特征,避免一些key的hashCode高位不同,低位相同,造成hash冲突。
HashMap扩容
扩容过程
HashMap有一个负载因子,默认0.75,当容量达到最大容量0.75时,发生扩容,新的容量为原来的两倍。然后遍历老的数组,当数组结点只有一个元素时,直接通过hash计算放入新的数组;当数组结点是红黑树时,进行红黑树的处理;当数组结点时一个链表时,遍历链表,根据hash&(2\length)是0还是1判断放入oldIndex还是oldIndex+length。
扩容是否需要rehash
在Java8以后,不再需要rehash了,元素存储在数组中的位置是根据hash%length来决定的,扩容之后length变成2*length,由于length是2的N次幂,hash&(2*length)的最后结果只有0或者1,当是0时,元素在数组中的位置还是之前的oldIndex,当是1时,元素在数组中的位置变成了oldIndex+length。(这个在上面的源码中也体现了)。
HashMap的容量必须是2的N次幂,因为:
- 计算数组位置时,因为hash&(length-1)=hash%length,可以通过hash&(length-1)来计算,位运算的效率更高。
- 方便扩容时不用rehash,直接根据hash&(2*length)的结果是0还是1来判断新的位置。
ConcurrentHashMap
Java8的ConcurrentHashMap底层结构和HashMap是一致的,不过由于要保证线程安全,使用了cas和synchronized锁。Java7的ConcurrentHashMap使用了分段锁,引入了Segment,一个ConcurrentHashMap由Segment数组组成,Segment继承了ReentrantLock来进行加锁,所以每次操作时只需要对每个Segment进行加锁,其他Segment不受影响,这样并发度就高了。
put方法分析
1 | public V put(K key, V value) { |
初始化table
1 | private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() { |